Introduction
Definition of 3D Modelers
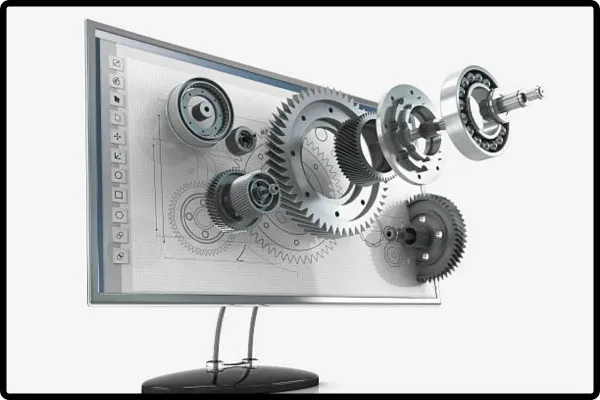

3D modelers are professionals who specialize in creating three-dimensional digital representations. They create models of objects, people, places, and ideas. They create these models using sophisticated software, enabling 3D viewing and manipulation. In simple terms, 3D modelers use virtual reality to bring ideas and concepts to life.
The process of 3D modeling involves creating a wireframe or skeleton. Adding surfaces, textures, and other features makes an item appear realistic and visually appealing. These models can range in complexity from simple shapes to detailed designs.
3D modellers play an important role in various industries. They are a vital component of today’s digital world. Their work is invaluable.
- Entertainment and Gaming
In the entertainment and gaming industry, 3D modellers create characters, objects, and entire virtual worlds. These models are necessary for creating beautiful movies, TV shows, animations, and video games.
- Architecture and Construction 3D modelers play an important role in architectural visualization. They also contribute to building prototyping. They turn architectural designs into 3D models. This allows architects, clients, and builders to see their projects. They can make changes before construction starts.
- Manufacturers and engineers rely on 3D modelers to develop prototypes. They also use 3D models to visualize product designs. Additionally, they rely on 3D models to streamline production processes. This relies on computer-aided design (CAD) integration. It’s a crucial component that supports the development of precise and functional products.
- Medical and Healthcare
In the medical industry, 3D modellers help with surgical planning. They also help develop prototypes for medical devices. These simulations help medical personnel visualize and practice complex procedures. As a result, patient outcomes improve.
C. Purpose of 3D Modeling. The main goal of 3D modeling is to transform abstract thoughts or designs into tangible digital representations. It does a number of vital tasks.
3D models offer a realistic way to visualize ideas, designs, and products. You can see them before they are physically created. This helps with decision making and lowers the possibility of expensive mistakes.
Fields like manufacturing and medicine use 3D models for rapid prototyping. They enable the development and testing of real prototypes based on digital designs.
3D models act as a universal visual language. They communicate intricate concepts and designs to clients, collaborators, and stakeholders.
Innovation: 3D modelling pushes the limits of invention and creativity. It makes it possible to create brand-new goods. It also allows for making works of art and interactive experiences.
Navigating the World of 3D Modelers: Types, Roles, and Trends
II. Types of 3D Modelers A. Professional 3D Modelers

- Professional 3D modelers are individuals who specialize in building 3D models. Their duties and job roles can change based on the sector they work in. Some typical roles include.
Character modelers focus on producing 3D characters for animations, video games, and movies. They specialize in facial expressions, anatomy, and character design.
Environmental Modelers.
Environmental modelers create immersive virtual environments. They design the architecture, landscape, and other elements for simulations. They also design for movies and video games.

Product modelers
Product Modelers build precise 3D models of physical products. They do this in the areas of product design and manufacturing. This helps with visualization and prototyping.
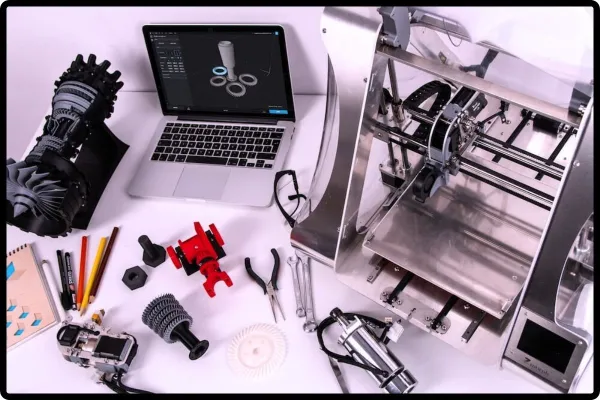

Architects and architectural firms use 3D models to bring building plans to life in 3D. Architectural modelers call them. They use the models for presentations to clients and project planning.
- Professional 3D modelers use specialized software tools to construct their work. Some of the most popular software tools are.
Autodesk Maya: Often used for character modelling and animation in the entertainment industry.
Blender is open-source software. You can use it for various 3D modeling needs, such as creating characters and animating them.
ZBrush is frequently used in the video game and film industries. The highly detailed character and creature modeling is well-known.
SolidWorks is often used in engineering and product design. It creates accurate 3D representations of mechanical parts.
B. Hobbyist 3D Modelers
- Hobbyist 3D modelers design 3D models for their own enjoyment and artistic expression. They use 3D models creatively. They may use 3D modeling as a hobby, a means of artistic expression, or as a component of a DIY project. Creative uses for hobbyist 3D modelers include:
Many hobbyists use 3D modeling to create original sculptures and works of art. 3D printers can make these.
Hobbyists can use 3D modelling to design complex costume props and accessories. They can also produce them. They use it for cosplay and prop making. They do this for cosplay and costume creation.
- Many people find that 3D modeling is a useful tool for learning and skill improvement. This medium allows hobbyists to investigate computer animation, graphics, and design. Learning 3D modeling can serve as a springboard for more challenging creative projects. It may also lead to a change in employment.
III. Industries and Applications A. Entertainment and Gaming
- In the entertainment and gaming industry, 3D modellers bring characters to life. These styles range from resembling people to being strange monsters. Character modellers concentrate on producing minute details, realistic animations, and lifelike expressions. They do this to improve the player or spectator experience.
- 3D modellers create the environment and objects in video games and virtual worlds. They also create assets. They design the environments, structures, vehicles, weapons, and other items. They ensure these elements fit with the game’s story and aesthetics. Immersive and visually appealing environments are essential for captivating players.
B. Architecture and Construction
- Architectural modelers play an important role in the visualization of architecture. They turn building concepts and blueprints into virtual, interactive 3D models. This helps architects, clients, and stakeholders better understand the proposed structure, spatial arrangements, and materials.
- Building prototypes requires creating 3D models. Architects and engineers use these models to test and improve their designs. They ensure the designs are structurally sound and functional before construction begins. This can lead to cost savings and more efficient building processes.
C. Manufacturing and Engineering
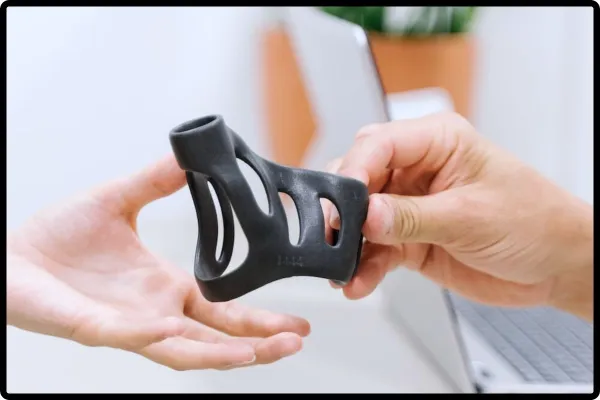

- In manufacturing and engineering, 3D modellers produce accurate prototypes of products, machinery, and components. Digital models make it easier to test and confirm designs before physical manufacturing. They lower errors and optimize effectiveness and performance.
- CAD is important in many industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Integration with computers is key. Engineers and 3D modellers work together to produce accurate CAD models. These models serve as production plans for sophisticated gear and systems.
D. Medical and Healthcare
- In the medical field, 3D modelers help surgeons plan surgeries. They build anatomically correct representations of patients’ organs and structures. Surgeons use these models to improve precision and lower surgical risks. They use them during preoperative preparation.
- 3D modeling is also used in the creation of medical equipment and prosthetics. It’s used in medical device prototyping too. Specialists can design for patient needs. We can test and improve 3D printed prototypes.
Exploring 3D Modeling: Skills, Education, Challenges, and Future Trends.
IV. Skills Required A. Technical Proficiency 1. A strong understanding of 3D modeling software is fundamental. You must be proficient with industry-specific tools like Maya, ZBrush, and Blender. 3D modelers must know modeling, texturing, lighting, and rendering techniques in these software applications.
2. Understanding the fundamentals of 3D printing is becoming more crucial. This is especially true in industries like manufacturing and healthcare. 3D modellers must consider how their digital creations transfer into actual objects. They must also account for printability and material constraints.

B. Creativity and Artistic Skills 1. Creating lifelike textures and rendering 3D models to make them look beautiful requires artistic skills. Texture painters use painting software to add depth, color, and surface details to models.
2. In entertainment and gaming, 3D modellers who animate characters must understand movement fundamentals. They also need to know about rigging and animation software. They need specialized skills to bring characters to life through movement and emotion.
C. Problem-Solving and Attention to Detail

3D modelers face technical difficulties in their work. They have to optimize performance, work around software constraints, and fix design defects. Successful problem solving requires problem-solving abilities. Attention to detail ensures that models are accurate and aesthetically appealing.
Navigating the World of 3D Modeling: Education, Challenges, and Future Trends”
Aspiring 3D modelers can pursue academic degrees in related fields, such as:
Bachelor’s Degrees often cover 3D modelling in depth. This is common in programs for computer animation, digital arts, or game design. These degrees offer a comprehensive foundation in both the technical and aesthetic fields.
Several universities offer master’s degrees in computer graphics. These programs explore advanced 3D modeling techniques and research.
B. Online Courses and Tutorials
Many online platforms provide courses and tutorials on 3D modeling. This makes it accessible to a wide audience. Websites like Udemy, Coursera, and Linkedin Learning offer courses for beginners and experienced students.
C. Workshops and Industry Certifications
Aspiring 3D modellers can attend workshops, seminars, and training courses tailored to their business. They can gain expertise in the field and connect with experts. Industry certifications, like Autodesk Certified Professional, also confirm skills and improve job opportunities.
Challenges, Trends, and Career Opportunities in 3D Modeling
Challenges, Trends, and Career Opportunities in 3D Modeling”
VI. Challenges in 3D Modeling: Hardware and Software Limitations. 3D modeling often requires powerful computers. They need high-end graphics cards and plenty of RAM. This will help them handle difficult tasks effectively. Keeping hardware up to date can be difficult. This is especially true for independent artists or amateurs.
Additionally, software restrictions might sometimes make the creative process more difficult. For example, complex scenes or highly detailed models may strain 3D modeling software. This can cause performance problems.
B. Complex Projects and Deadlines
In professional settings, 3D modellers regularly work on challenging projects with tight deadlines. Satisfying customer expectations while maintaining quality standards might be challenging. To overcome these obstacles, you will need strong time and project management abilities.
C. Keeping up with evolving technology: The field of 3D modeling is always changing. It’s common for new software tools, methods, and trends to emerge. Maintaining competitiveness and relevance in the sector requires keeping up with these developments.
Future Trends in 3D Modeling and Career Opportunities”
VII. Future Trends A. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
Integrating 3D modeling with VR and AR is a prominent trend. 3D models are essential in creating immersive virtual and augmented experiences. Interactive games, architectural walkthroughs, and training simulations use them.
AI and Automation in 3D Modeling. 3D modelers are increasingly using artificial intelligence (AI). It can automate repetitive tasks. For example, creating complex textures and optimizing models for different platforms. AI-driven technologies streamline workflows and increase production.
C. Sustainability and 3D Printing
Sustainability is gaining importance in 3D modeling. Designing products with low waste and environmental impact is gaining prominence. 3D printing’s potential for local, on-demand manufacturing can help with these sustainability goals.

Exploring Career Opportunities in 3D Modeling
VIII. A 3D Modeler makes 3D models for characters, environments, goods, or architectural projects.
Texture Artists enhance 3D models with textures and other visual elements. They make the models more appealing and realistic.
A rigging artist specializes in building the skeletons and control system (rigs). Rigs enable the movement and animation of 3D characters.
An environment artist creates the virtual worlds and settings within games and simulations. They also build them.
A CAD Modeler works with engineers and architects. They create thorough CAD models for architectural and engineering projects.
3D modellers have the option to choose between full-time employment and freelancing.
Freelancers enjoy independence. They work on a variety of assignments for different clients. They must handle their own commercial concerns. But, they are free to determine their own fees and schedules.
Full-time Employment:
Working for a studio, business, or agency provides stability and benefits. It also offers the chance to work with others on bigger projects. But, it could restrict artistic freedom.
The salaries of 3D modelers vary greatly. This depends on experience, location, and industry.
Entry-level 3D modellers should expect low income. It is usually in the range of $40,000 to $60,000 annually.
Mid-Level: Those with a few years of expertise can expect to make between $60,000 and $80,000 per year.
Experienced 3D modelers can earn over $100,000 annually. This is especially true for those in specialized sectors.
Exploring Influential 3D Modelers and Studios
IX. Famous 3D modelers and their work. A. Notable artists and studios. Pixar Animation Studios has earned a reputation for creating groundbreaking animated works. Examples include “Toy Story” and “Finding Nemo.” Its team of extraordinarily gifted 3D artists has raised the bar for the industry.
Industrial Light & Magic (ILM) is a division of Lucasfilm. It is well known for its visual effects work in the Star Wars saga and other big budget films. Their artists have pushed the limits of CGI and 3D modelling.
Blizzard Entertainment has a reputation for creating legendary video games. Examples include World of Warcraft and Overwatch. The company’s 3D designers have a reputation for creating complex character designs. They are also renowned for creating immersive landscapes.
Motion capture and 3D modeling brought Gollum to life in “The Lord of the Rings” film trilogy. Andy Serkis played Gollum. Andy Serkis played Gollum. It used Andy Serkis as Gollum. This showcased the possibilities of 3D in character animation.
Mars Rovers, Curiosity and Perseverance, use 3D models and simulations to plan their missions on Mars. They also use them to carry out their missions. NASA operates the rovers.
“Avatar” (2009): James Cameron’s “Avatar” revolutionized 3D filmmaking. It used cutting edge 3D modeling and CGI to depict Pandora, a lush and alien planet.
Concluding the Journey: 3D Modelers and Their Opportunities
Conclusion: A Recap of the Importance of 3D Modelers. This comprehensive exploration has revealed how 3D modelers bring concepts to life in various industries. 3D modelers are essential to the visualisation of ideas, the improvement of designs, and the creation of immersive experiences in a variety of industries. These include entertainment, gaming, manufacturing, architecture, and healthcare.
B. Encouragement for Aspiring 3D Modelers
The field of 3D modeling has a balance of artistic and technical obstacles. For those considering a career in 3D modeling, this is important to know. The demand for skilled 3D modellers is growing. You may want to pursue it professionally or as a pastime.
Potential for Innovation and Creativity in the Field. As technology advances, new trends like VR, AR, and AI continue to change the industry. This gives 3D modellers more opportunity to create. They can push the limits of what is possible in the digital world. The future presents fascinating possibilities for individuals who are passionate about 3D modeling.
In conclusion, 3D modelers are the architects of the digital world. They design virtual environments, people, objects, and experiences that improve our lives. Their work fills the gap between fantasy and reality and impacts various industries. The world of 3D modeling is interesting. Whether you are a budding modeler or just interested in the industry. It is also full of opportunity.
